Melanoma is a type of cancer in which malignant cells form in the melanocytes (the cells that produce melanin or pigment in the skin). Melanoma can occur anywhere on the skin and can metastasize (spread) to other parts of the body. There are several subtypes of melanoma, including cutaneous, acral, mucosal, ocular, and even amelanotic melanoma.
Other risk factors include the presence of many moles, atypical moles, congenital melanocytic nevi (birthmarks or moles that are present at birth or develop shortly after), and familial conditions like Familial Atypical Multiple Mole Melanoma (FAMMM) syndrome. Additionally, hereditary factors, such as the CDKN2A gene mutation, Xeroderma Pigmentosum, Werner syndrome, and Retinoblastoma, can elevate the risk. Light-colored skin, eyes, and hair, a personal history of skin cancer, a family history of skin cancer, and a weakened immune system are also identified as significant risk factors.[2]
What does melanoma skin cancer look like?
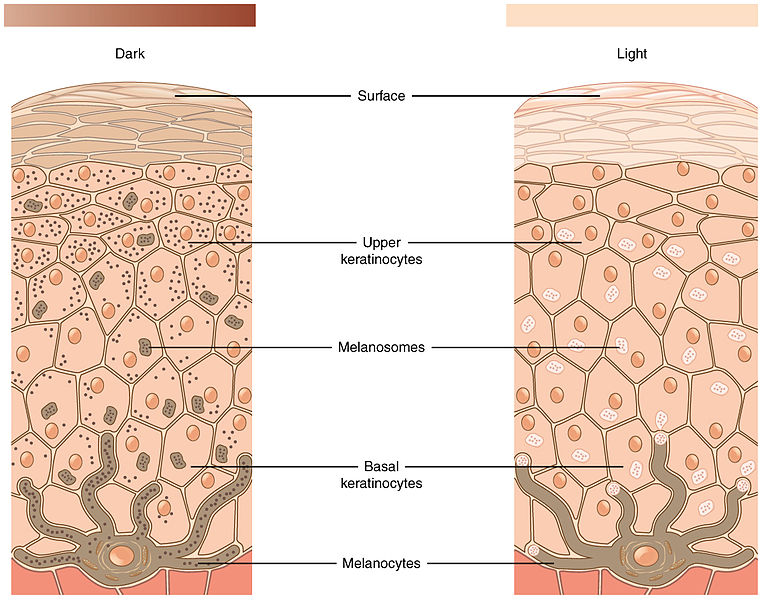
Not all melanomas have the same appearance. Depending on your skin colour, the melanoma might be brown, black, reddish, tan, sometimes even blue! Though most melanomas develop on normal-looking skin, some develop on existing moles. The best way to catch a melanoma early is to look for anything new, changing or unusual on your skin.
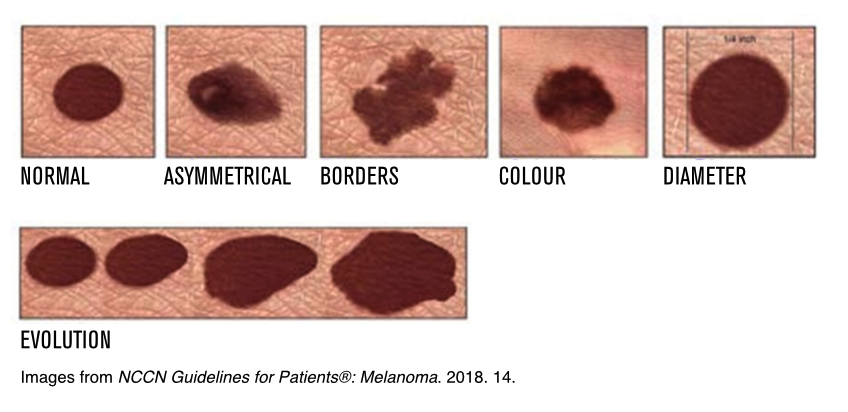 A common and effective tool to help you spot melanoma is the ABCDEs of Melanoma:
A common and effective tool to help you spot melanoma is the ABCDEs of Melanoma:
A stands for asymmetry, where one half of the lesion does not match the other in shape.
B stands for irregular borders; melanomas often have jagged or notched edges instead of smooth contours.
C stands for colour; melanomas sometimes have more than one colors within the lesion, such as brown, black, tan, red, blue, or white, in contrast to the more uniform shades seen in benign moles.
D stands for diameter, with melanomas tending to be larger than other moles, or grow larger over time.
E stands for evolving, highlighting the importance of observing any changes in texture, elevation, size, colour, or the development of symptoms like bleeding or itching.
Regular skin self-examinations and professional skin checks are vital for early detection, as prompt medical attention significantly improves the chances of successful melanoma treatment.
To learn more about performing a skin check, visit our Skin Check Guide page.
Is melanoma skin cancer dangerous?
Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of skin cancer. The Canadian Cancer Society estimates that it caused 1,200 deaths in Canada in 2022. The outlook for individuals with melanoma can vary significantly. Most melanomas can be cured if detected and treated before they have a chance to spread. Early detection and removal of melanoma are essential for a full recovery.
How is melanoma skin cancer treated?
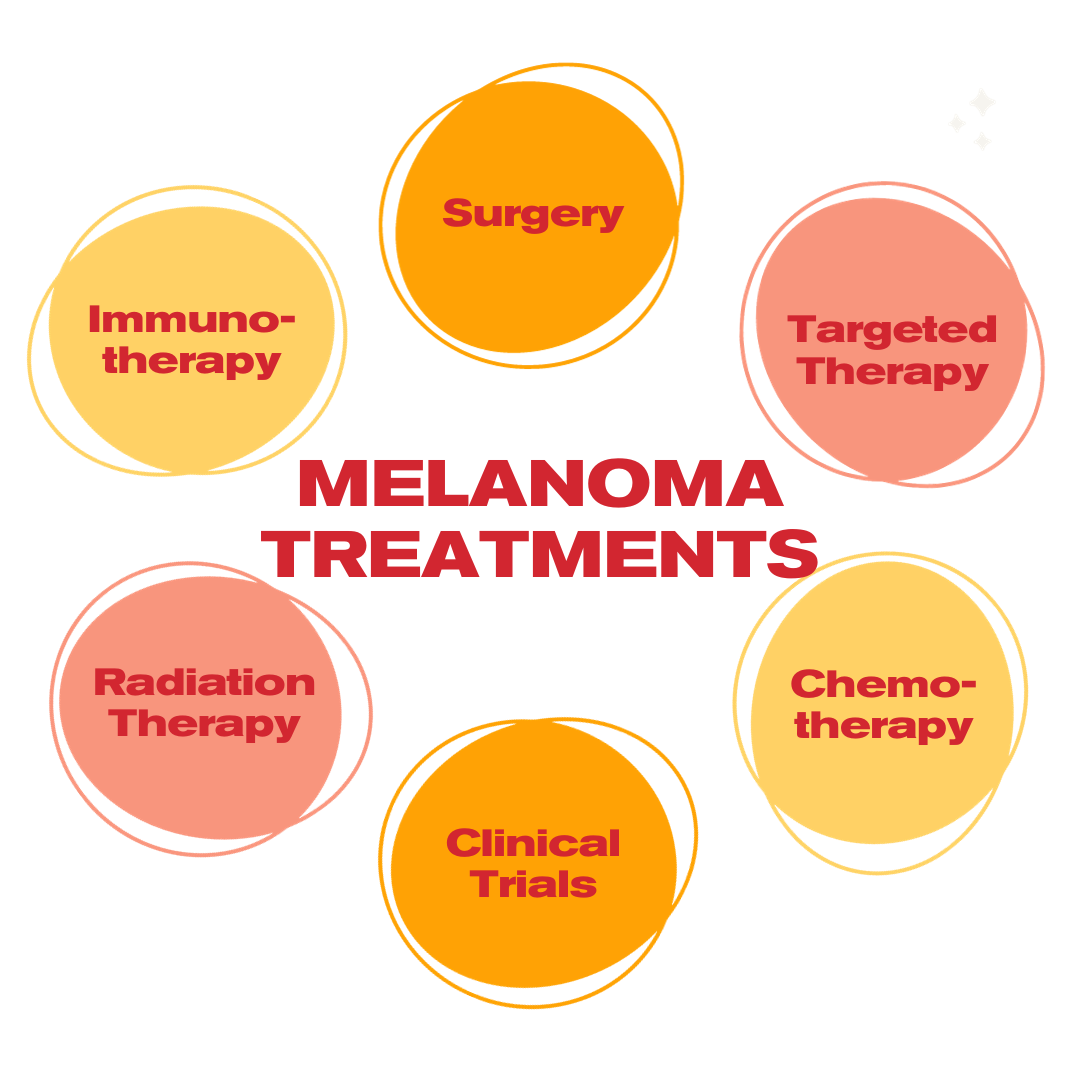
There are various treatment options for melanoma. When someone is diagnosed with melanoma, their healthcare team discusses the best melanoma treatments for them and works with them to develop a treatment plan. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted Therapy
- Radiation Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Clinical Trials


















 A common and effective tool to help you spot melanoma is the ABCDEs of Melanoma:
A common and effective tool to help you spot melanoma is the ABCDEs of Melanoma:












Dr. Joël Claveau is a dermatologist, specialized in the diagnosis and treatment of Melanoma and Skin Cancers, and an Associate Professor with the Department of Medicine at Laval University where he completed his Medical Study and Internal Medicine training. He did his residency in Dermatology at McGill University and subsequently worked at the Melanoma Clinic at the Royal Victoria Hospital in Montreal, Quebec. He is a diplomat of the American Board of Dermatology and is a member of a number of Medical Societies including the American Academy of Dermatology and the International Dermoscopy Society.
He has received awards including Honorary Member of La Société Française de Dermatologie, the Dermatologist’s Volunteer Award of the Canadian Dermatology Association (CDA) for his work on the prevention of skin cancers and the CDA Symposium of the year on two occasions (Dermoscopy). Since 1996, he has been the Director of the Melanoma and Skin Cancer Clinic at Le Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Hôtel-Dieu de Québec, and worked in Public Health for the province of Québec, especially on the new Tanning Bed Legislation. He participated to the publication of papers in peer-reviewed journals including work on melanoma, skin cancers and sunscreens. He is actively involved in various Continuing Medical Education events and investigator in many clinical trials on advanced and metastatic melanoma.